Herramienta médica para el Aprendizaje de Protocolos de Destete Ventilatorio.
Medical Learning Tool for Ventilator Weaning Protocols.
Barra lateral del artículo
Términos de la licencia (VER)

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
Declaración del copyright
Los autores ceden en exclusiva a la Universidad EIA, con facultad de cesión a terceros, todos los derechos de explotación que deriven de los trabajos que sean aceptados para su publicación en la Revista EIA, así como en cualquier producto derivados de la misma y, en particular, los de reproducción, distribución, comunicación pública (incluida la puesta a disposición interactiva) y transformación (incluidas la adaptación, la modificación y, en su caso, la traducción), para todas las modalidades de explotación (a título enunciativo y no limitativo: en formato papel, electrónico, on-line, soporte informático o audiovisual, así como en cualquier otro formato, incluso con finalidad promocional o publicitaria y/o para la realización de productos derivados), para un ámbito territorial mundial y para toda la duración legal de los derechos prevista en el vigente texto difundido de la Ley de Propiedad Intelectual. Esta cesión la realizarán los autores sin derecho a ningún tipo de remuneración o indemnización.
La autorización conferida a la Revista EIA estará vigente a partir de la fecha en que se incluye en el volumen y número respectivo en el Sistema Open Journal Systems de la Revista EIA, así como en las diferentes bases e índices de datos en que se encuentra indexada la publicación.
Todos los contenidos de la Revista EIA, están publicados bajo la Licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-NoDerivativa 4.0 Internacional
Licencia
![]()
Esta obra está bajo una Licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-NoDerivativa 4.0 Internacional
Contenido principal del artículo
Resumen
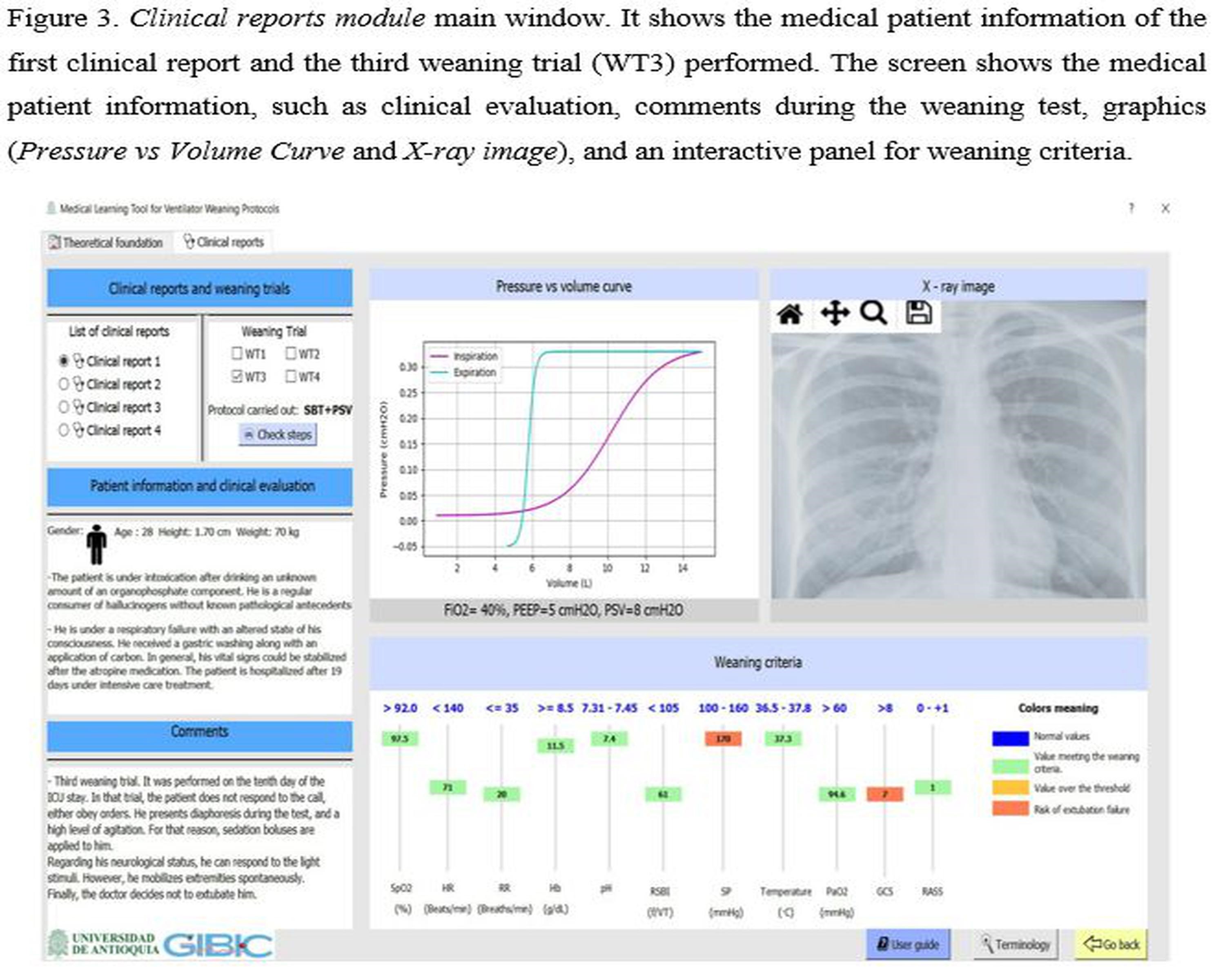
La ventilación mecánica es uno de los procedimientos médicos más usados en las unidades de cuidado intensivo alrededor del mundo. En la práctica clínica, este procedimiento representa un alto nivel de complejidad, especialmente en las fases de extubación y los protocolos de destete. Con el fin de mejorar las destrezas de estudiantes del área de la salud en esta temática, fue desarrollada una aplicación para el entrenamiento y aprendizaje de protocolos de destete ventilatorio. La aplicación cuenta con dos módulos gráficos, los cuales proporcionan el soporte teórico y un conjunto de casos clínicos de diferentes pacientes bajo pruebas de respiración espontanea. Adicionalmente, la aplicación incluye historias clínicas y un panel interactivo con la información de los protocolos de destete y la condición clínica
de los pacientes durante estas pruebas. Un test de usabilidad fue realizado a 12 sujetos con
el fin de validar la usabilidad y funcionalidad de la aplicación, donde se evidenció un alto
nivel de satisfacción de los usuarios con la aplicación, destacando la facilidad de abordar
conceptos críticos en ventilación mecánica de forma sencilla.
Descargas
Detalles del artículo
Juan Camilo Mesa Agudelo, Universidad de Antioquia
Juan Camilo Mesa Agudelo, oriundo del bello municipio de Santa Rosa de Osos
(Antioquia), lugar donde crecí e inicié mi formación como persona y profesional. En el año 2000
inicié mi formación educativa en la Institución Escuela Porfirio Barba Jacob, cuna del poeta
emblemático del norte Antioqueño. Allí tuve la oportunidad de desarrollar mis primeras
habilidades tales como escribir, leer y lo más importante a compartir y convivir en sociedad.
Durante mi estancia en esta institución fuí acreedor de diferentes reconocimientos académicos.
En el año 2006 culmine mi etapa de educación básica primaria.
En el año 2007, inicié mis estudios de básica secundaria en el Colegio Técnico Nuestra Señora
de las Misericordias, lugar donde aprendí y disfruté mi niñez y adolescencia. Allí tuve la
oportunidad de conocer algunos maestros y compañeros que marcaron mi vida, especialmente el
profe de matemáticas quien impulsó en mí el espíritu de ser Ingeniero y servir a la sociedad a
partir de la ciencia, la física y las matemáticas. Por tanto, decidí aplicar a una ingeniería que
tuviese un gran compromiso con la vida, especialmente una que presentara un enfoque directo
con el cuidado y preservación de la vida humana a partir de innovadores soluciones tales como
dispositivos, aplicaciones móviles, entre otras herramientas tecnológicas.
Maria Bernarda Salazar Sánchez, Universidad de Antioquia
Maria Bernarda Salazar es Bioingeniera (2011) y Doctora en Ingeniería Electrónica (2018) de la Universidad de Antioquia. Actualmente es Profesora Universitaria Ocasional del Programa de Bioingeniería de la Universidad de Antioquia y lidera el desarrollo del Primer Proyecto Intregrativo de Semestre de dicho programa académico. Forma parte del grupo de Investigación Bioinstrumentation and Clinical Engineering Research Group (GIBIC- www.gibicgroup.com) de la misma Universidad en Medellín, Colombia en la línea respiratoria, modelado y procesamiento de señales.
Su actividad docente se enfoca en las áreas de Teoría de Modelos, Simulación de Sistemas, Procesamiento de Señales Biomédicas, Análisis de Circuitos y Electrónica Analógica. Su actividad de investigación se concentra en el análisis, modelado, procesamiento de señales y desarrollo de aplicaciones a los campos del sistema respiratorio y cardiovascular en su interacción con el ventilador mecánico. También participa en proyectos de investigación en el campo de entrenamiento médico.
Referencias (VER)
Alhaqwi, A. I. and Taha, W. S. (2015) ‘Promoting excellence in teaching and learning in clinical education’, Journal of Taibah University Medical Sciences. Elsevier Ltd, 10(1), pp. 97–101. https:// doi.org/10.1016/j.jtumed.2015.02.005.
Alroobaea, R. and Mayhew, P. J. (2014) ‘How many participants are really enough for usability studies?’, Proceedings of 2014 Science and Information Conference, SAI 2014. The Science and Information (SAI) Organization, pp. 48–56. https:// doi.org/10.1109/SAI.2014.6918171.
Blackwood, B., Alderdice, F., Burns, K., Cardwell, C., Lavery, G. and O’Halloran, P. (2011) ‘Use of weaning protocols for reducing duration of mechanical ventilation in critically ill adult patients:Cochrane systematic review and meta-analysis’, Bmj, 342(7790), p. 214.
https:// doi.org/10.1136/bmj.c7237.
Branson, R. D. (2018) ‘Automation of Mechanical Ventilation’, Critical Care Clinics, 34(3), pp. 383–394. https:// doi.org/10.1016/j.ccc.2018.03.012.
Cohen, J., Shapiro, M., Grozovski, E., Fox, B., Lev, S. and Singer, P. (2009) ‘Prediction of extubation outcome: A randomised, controlled trial with automatic tube compensation vs. pressure support ventilation’, Critical Care, 13(1), pp. 1–7. https:// doi.org/10.1186/cc7724.
Correa-Gutierrez, S. J., Castro-Gutierrez, D. J. and Vera-Rondón, S. J. (2008) ‘Destete Ventilatorio Un Enfoque Fisioterapeutico Ventilatory Weaning a Physiotherapist Approach’, Movimiento científico, 2(1), p. 24. https:// doi.org/10.33881/2011-7191.%25x.
Danckers, M., Grosu, H., Jean, R., Cruz, R. B., Fidellaga, A., Han, Q., Awerbuch, E., Jadhav, N., Rose, K. and Khouli, H. (2013) ‘Nurse-driven, protocol-directed weaning from mechanical ventilation improves clinical outcomes and is well accepted by intensive care unit physicians’, Journal of Critical Care. Elsevier Inc., 28(4), pp. 433–441.
https:// doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2012.10.012.
DDSurgical (2020) ‘Basics of Mechanical Ventilation’.
https://apps.apple.com/us/app/basics-of-mechanical-ventilation/id671298263.
De-Miguel-Díez, J., Jiménez-García, R., Hernández-Barrera, V., Zamorano-Leon, J. J., Villanueva-Orbaiz, R., Albaladejo-Vicente, R. and López-de-Andrés, A. (2019) ‘Trends in mechanical ventilation use and mortality over time in patients receiving mechanical ventilation in Spain from 2001 to 2015.’, European Journal of Internal Medicine. Elsevier, 74(September 2019), pp. 67–72. https:// doi.org/10.1016/j.ejim.2019.11.023.
Florek, A. G. and Dellavalle, R. P. (2016) ‘Case reports in medical education: A platform for training medical students, residents, and fellows in scientific writing and critical thinking’, Journal of Medical Case Reports. Journal of Medical Case Reports, 10(1), pp. 1–3.
https:// doi.org/10.1186/s13256-016-0851-5.
Hansen, B. S. and Severinsson, E. (2007) ‘Intensive care nurses’ perceptions of protocol-directed weaning-A qualitative study’, Intensive and Critical Care Nursing, 23(4), pp. 196–205. https:// doi.org/10.1016/j.iccn.2007.03.001.
Hashemian, S. M., Mortaz, E., Jamaati, H., Bagheri, L., Mohajerani, S. A., Garssen, J., Movassaghi, M., Barnes, P. J., Hill, N. S. and Adcock, I. M. (2018) ‘Budesonide facilitates weaning from mechanical ventilation in difficult-to-wean very severe COPD patients: Association with inflammatory mediators and cells’, Journal of Critical Care, 44, pp. 161–167. https:// doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2017.10.045.
Hernández-Valdivieso, A. M., Salazar-Sánchez, M. B., Urrego-Higuita, D. A., Costa-Castelló, R. and Mañanas-Villanueva, M. A. (2011) ‘Virtual laboratory for simulation and learning of cardiovascular system function in BME studies’, Revista Facultad de Ingenieria, (60), pp. 194–201.
Ibrahim, R. (2018) ‘Mechanical Ventilation Advanced’. https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=soooooonandroid.mechanicalventilationadvanced&hl=en.
Kogler, V. M. (2009) ‘Advantage of spontaneous breathing in patients with respiratory failure’, Signa Vitae, 4(1), pp. 10–13. https:// doi.org/10.22514/SV41.042009.2.
MacIntyre, N. R. (2001) ‘Evidence-Based Guidelines for Weaning and Discontinuing Ventilatory Support: A Collective Task Force Facilitated by the American College of Chest Physicians; the American Association for Respiratory Care; and the American College of Critical Care Medicine’, Chest, 120(6, Supplement), pp. 375S-395S.
https:// doi.org/10.1378/chest.120.6_suppl.375S.
Medtronic (2020a) Ventilator Weaning Management, Challenges with ventilator weaning management. Available at: https://www.medtronic.com/covidien/en-us/clinical-solutions/weaning-management/challenges-with-weaning-management.html.
Medtronic (2020b) Vital SyncTM Monitoring and CDS Solution Clinical Value. Available at: https://www.medtronic.com/covidien/en-us/products/health-informatics-and-monitoring/vital-sync-monitoring-and-cds-solution/clinical-value.html.
Nagata, I., Takei, T., Hatakeyama, J., Toh, M., Yamada, H. and Fujisawa, M. (2019) ‘Clinical features and outcomes of prolonged mechanical ventilation: a single-center retrospective observational study’, JA Clinical Reports. JA Clinical Reports, 5(1).
https:// doi.org/10.1186/s40981-019-0284-4.
Salazar-Sánchez, M. B., Hernández-Valdivieso, A. M., Botero-Ospina, A. F. and Cortés-Daza, C. C. (2017) ‘Learning Tool for Mechanical Ventilation during Spontaneous Breathing Test on Patients Intoxicated with Pesticides’, in Torres, I., Bustamante, J., and Sierra, D. A. (eds) VII Latin American Congress on Biomedical Engineering CLAIB 2016, Bucaramanga, Santander, Colombia, October 26th -28th, 2016. Singapore: Springer Singapore, pp. 248–251.
Salazar-Sánchez, M. B., Hernández-Valdivieso, A. M., Rodríguez-López, C., Mesa-Agudelo, J. C., Muñoz-Ortega, I. C., Serna-Higuita, L. Y. and Buitrago-Castro, L. F. (2019) ‘Areas with the Highest Use of Simulator for Health Education in Colombia’, Communications in Computer and Information Science, 1052, pp. 643–652.
https:// doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-31019-6_54.
Serna, L. Y., Hernandez, A. M. and Mañanas, M. A. (2010) ‘Computational tool for modeling and simulation of mechanically ventilated patients’, 2010 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBC’10, (August), pp. 569–572. https:// doi.org/10.1109/IEMBS.2010.5626429.
Stahl, C., Dahmen, G., Ziegler, A. and Muhl, E. (2009) ‘Comparison of automated protocol-based versus non-protocol-based physician-directed weaning from mechanical ventilationVergleich von automatisierter protokollbasierter mit arztgesteuerter nicht protokollbasierter Entwöhnung vom Beatmungsgerät’, Intensivmedizin und Notfallmedizin, 46(6), pp. 441–446. https:// doi.org/10.1007/s00390-009-0061-0.
TruCorp (2020) ‘TruVent App’. Available at: https://www.trucorp.com/P/144/TruVentApp.
Yousefi, H., Toghyani, F., Yazdannik, A. R. and Fazel, K. (2015) ‘Effect of using Richmond Agitation Sedation Scale on duration of mechanical ventilation, type and dosage of sedation on hospitalized patients in intensive care units.’, Iranian journal of nursing and midwifery research, 20(6), pp. 700–704. https:// doi.org/10.4103/1735-9066.170008.
Zein, H., Baratloo, A., Negida, A. and Safari, S. (2016) ‘Ventilator Weaning and Spontaneous Breathing Trials; an Educational Review.’, Emergency (Tehran, Iran), 4(2), pp. 65–71. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4893753/.

 PDF
PDF
 FLIP
FLIP