Simulación de procesos y evaluación ambiental de la producción de un bioadsorbente modificado con quelantes y nanopartículas magnéticas
Process simulation and environmental assessment of the mass production of a modified bioadsorbent with chelants and magnetic nanoparticles
Barra lateral del artículo
Términos de la licencia (VER)

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
Declaración del copyright
Los autores ceden en exclusiva a la Universidad EIA, con facultad de cesión a terceros, todos los derechos de explotación que deriven de los trabajos que sean aceptados para su publicación en la Revista EIA, así como en cualquier producto derivados de la misma y, en particular, los de reproducción, distribución, comunicación pública (incluida la puesta a disposición interactiva) y transformación (incluidas la adaptación, la modificación y, en su caso, la traducción), para todas las modalidades de explotación (a título enunciativo y no limitativo: en formato papel, electrónico, on-line, soporte informático o audiovisual, así como en cualquier otro formato, incluso con finalidad promocional o publicitaria y/o para la realización de productos derivados), para un ámbito territorial mundial y para toda la duración legal de los derechos prevista en el vigente texto difundido de la Ley de Propiedad Intelectual. Esta cesión la realizarán los autores sin derecho a ningún tipo de remuneración o indemnización.
La autorización conferida a la Revista EIA estará vigente a partir de la fecha en que se incluye en el volumen y número respectivo en el Sistema Open Journal Systems de la Revista EIA, así como en las diferentes bases e índices de datos en que se encuentra indexada la publicación.
Todos los contenidos de la Revista EIA, están publicados bajo la Licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-NoDerivativa 4.0 Internacional
Licencia
![]()
Esta obra está bajo una Licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-NoDerivativa 4.0 Internacional
Contenido principal del artículo
Resumen
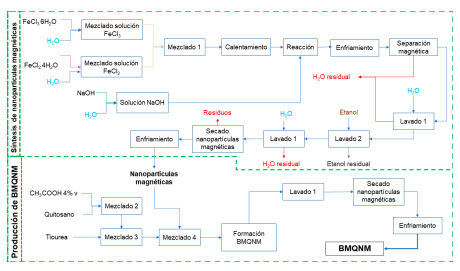
Las estrategias de valorización de residuos son clave para lograr una producción más sostenible dentro de la industria de mariscos. El quitosano es un biopolímero que cuenta con múltiples aplicaciones en sectores como agricultura, la industria alimentaria, cosmética, sistemas detratamiento de agua, entre otros. Los residuos de la industria de los mariscos pueden ser aprovechados en la síntesis de quitosano, convirtiéndose en una alternativa de valorización de residuos. Uno de los usos alternativos del quitosano es como precursor para la preparación de bioadsorbentes modificados con el fin de eliminar contaminantes. En este trabajo, se desarrolló la evaluación ambiental del proceso de obtención a escala industrial de un bioadsorbente de quitosano funcionalizado con nanopartículas de magnetita y un quelante (tiourea), con el objetivo de evaluar los posibles impactos ambientales. Se utilizó el software Aspen Plus ® para la simulación del proceso, que permite la cuantificación de flujos másicos y estimación de propiedades. El análisis ambiental se realizó utilizando el Algoritmo de Reducción de Residuos (WAR) a través del software WAR GUI. Los resultados mostraron que el proceso consume impactos ambientales potenciales (PEI), obteniendo un valor positivo de 1.870 PEI/h. Las categorías relacionadas con los impactos toxicológicos (HTPI, HTPE, TTP y ATP) presentaron menores valores que las relacionadas con impactos atmosféricos (GWP, ODP, PCOP y AP), siendo las de mayor contribución toxicidad humana por ingestión (HTPI) y la toxicidad potencial terrestre (TTP), categorías que se encuentran asociadas a la dosis letal media (LD50) de los compuestos involucrados en el proceso. Se determinó consumo de PEI usando como fuente energética gas natural.
Descargas
Detalles del artículo
Referencias (VER)
Acosta-Ferreira, S., Castillo, O. S., Madera-Santana, J. T., Mendoza-García, D. A., Núñez-Colín, C. A., Grijalva-Verdugo, C., Villa-Lerma, A. G., Morales-Vargas, A. T., & Rodríguez-Núñez, J. R. (2020). Production and physicochemical characterization of chitosan for the harvesting of wild microalgae consortia. Biotechnology Reports, 28, e00554. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BTRE.2020.E00554
Aguilar Vásquez, E., & González-Delgado, Á. (2021). Evaluación ambiental de la producción de microperlas de quitosano modificadas con TiO2 y magnetita usando el algoritmo de reducción de residuos (WAR). Revista ION, 34(1), 121–136. https://doi.org/10.18273/revion.v34n1-2021010
Alfaro, I., Molina, L., González, P., Gaete, J., Valenzuela, F., Marco, J. F., Sáez, C., & Basualto, C. (2019). Silica-coated magnetite nanoparticles functionalized with betaine and their use as an adsorbent for Mo(VI) and Re(VII) species from acidic aqueous solutions. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 78, 271–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2019.06.002
Arteaga-Díaz, S., Sanjuan-Acosta, M. J., & González-Delgado, Á. (2018). Computer-aided environmental evaluation of bioethanol production from empty palm fruit bunches using oxalic acid pretreatment and molecular sieves. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 70, 2113–2118. https://doi.org/10.3303/CET1870353
Asab, G., Zereffa, E. A., & Abdo Seghne, T. (2020). Synthesis of Silica-Coated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles by Microemulsion Method: Characterization and Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity. International Journal of Biomaterials, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4783612
Bilal, M., Ihsanullah, I., Younas, M., & Ul Hassan Shah, M. (2021). Recent advances in applications of low-cost adsorbents for the removal of heavy metals from water: A critical review. Separation and Purification Technology, 278, 119510. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SEPPUR.2021.119510
Bui, T. Q., Ton, S. N. C., Duong, A. T., & Tran, H. T. (2018). Size-dependent magnetic responsiveness of magnetite nanoparticles synthesised by co-precipitation and solvothermal methods. Journal of Science: Advanced Materials and Devices, 3(1), 107–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsamd.2017.11.002
Carlson, E. C. (1996). Don’t Gamble With Physical Properties. Chemical Engineering Progress, October, 35–46.
Chai, W. S., Cheun, J. Y., Kumar, P. S., Mubashir, M., Majeed, Z., Banat, F., Ho, S. H., & Show, P. L. (2021). A review on conventional and novel materials towards heavy metal adsorption in wastewater treatment application. Journal of Cleaner Production, 296, 126589. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2021.126589
Cogollo-Herrera, K., Bonfante-Álvarez, H., De Ávila-Montiel, G., Barros, A. H., & González-Delgado, Á. D. (2018). Techno-economic sensitivity analysis of large scale chitosan production process from shrimp shell wastes. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 70, 2179–2184. https://doi.org/10.3303/CET1870364
Dos Santos, L. N., Santos, A. S., Dantas, K. D. G. F., & Ferreira, N. R. (2022). Adsorption of Cu (II) Ions Present in the Distilled Beverage (Sugar Cane Spirit) Using Chitosan Derived from the Shrimp Shell. Polymers 2022, Vol. 14, Page 573, 14(3), 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/POLYM14030573
González-Delgado, A., Cartagena, U. de, & SENA, S. N. de A. (2016). Remoción de Hidrocarburos aromáticos policíclicos (HAPs), presentes en aguas costeras de la bahía de Cartagena mediante la utilización de exoesqueleto de camarón como fuente de bioadsorbentes modificados con nanoparticulas (p. 30).
González-Delgado, Á. D., Moreno-sader, K. A., & Martínez-Consuegra, J. D. (2022). Biorrefinación sostenible del camarón : desarrollos desde la Ingeniería de Procesos Asistida por Computador.
Hadadian, Y., Sampaio, D. R. T., Ramos, A. P., Carneiro, A. A. O., Mozaffari, M., Cabrelli, L. C., & Pavan, T. Z. (2018). Synthesis and characterization of zinc substituted magnetite nanoparticles and their application to magneto-motive ultrasound imaging. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 465(May), 33–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.05.069
IDEAM. (2018). Carácterísticas Climatológicas De Ciudades Principales Y Municipios Turísticos. Instituto de Hidrología, Meteorología y Estudios Ambientales, 48. https://doi.org/http://www.ideam.gov.co/documents/21021/21789/1Sitios+turisticos2.pdf/cd4106e9-d608-4c29-91cc-16bee9151ddd
Karimi, M. H., Mahdavinia, G. R., Massoumi, B., Baghban, A., & Saraei, M. (2018). Ionically crosslinked magnetic chitosan/κ-carrageenan bioadsorbents for removal of anionic eriochrome black-T. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 113, 361–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.02.102
Kou, S. (Gabriel), Peters, L. M., & Mucalo, M. R. (2021). Chitosan: A review of sources and preparation methods. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 169, 85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2020.12.005
Li, J. L., Li, D. C., Zhang, S. L., Cui, H. C., & Wang, C. (2011). Analysis of the factors affecting the magnetic characteristics of nano-Fe 3 O 4 particles. Chinese Science Bulletin, 56(8), 803–810. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-010-4126-z
Meramo-Hurtado, S., Urbina-Suaréz, N., & González-Delgado, Á. (2019). Computer-aided environmental and exergy analyses of a large-scale production of chitosan microbeads modified with TiO2 nanoparticles. Journal of Cleaner Production, 237, 117804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117804
Miron, A., Sarbu, A., Zaharia, A., Sandu, T., Iovu, H., Fierascu, R. C., Neagu, A.-L., Chiriac, A.-L., & Iordache, T.-V. (2022). A Top-Down Procedure for Synthesizing Calcium Carbonate-Enriched Chitosan from Shrimp Shell Wastes. Gels, 8(11), 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/GELS8110742
Moreno-Sader, K. A., Martínez-Consuegra, J., & González-Delgado, Á. D. (2021). An integrated biorefinery approach via material recycle/reuse networks for the extraction of value-added components from shrimp: Computer-aided simulation and environmental assessment. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 127, 443–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FBP.2021.04.003
Moreno-Sader, K., Meramo-Hurtado, S., & González-Delgado, A. (2019). Computer-aided environmental and exergy analysis as decision-making tools for selecting bio-oil feedstocks. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 112(February), 42–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.05.044
Niculescu, A. G., Chircov, C., & Grumezescu, A. M. (2022). Magnetite nanoparticles: Synthesis methods – A comparative review. Methods, 199, 16–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.YMETH.2021.04.018
Okolie, J. A., Nanda, S., Dalai, A. K., & Kozinski, J. A. (2021). Techno-economic evaluation and sensitivity analysis of a conceptual design for supercritical water gasification of soybean straw to produce hydrogen. Bioresource Technology, 331, 125005. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2021.125005
Pereira da Silva, A. K., Cardoso, A., Benício de Sá Filho, E., Monteiro Cordeiro de Azeredo, H., Freire, F., Casimiro Filho, F., & Brito de Figueirêdo, M. C. (2021). Integrating life cycle assessment in early process development stage: The case of extracting starch from mango kernel. Journal of Cleaner Production, 321, 128981. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2021.128981
Pourmortazavi, S. M., Sahebi, H., Zandavar, H., & Mirsadeghi, S. (2019). Fabrication of Fe3O4 nanoparticles coated by extracted shrimp peels chitosan as sustainable adsorbents for removal of chromium contaminates from wastewater: The design of experiment. Composites Part B: Engineering, 175(June), 107130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107130
Qamar, S. A., Ashiq, M., Jahangeer, M., Riasat, A., & Bilal, M. (2020). Chitosan-based hybrid materials as adsorbents for textile dyes–A review. Case Studies in Chemical and Environmental Engineering, 2, 100021. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CSCEE.2020.100021
Qiu, N., Liu, Y., Xiang, M., Lu, X., Yang, Q., & Guo, R. (2018). A facile and stable colorimetric sensor based on three-dimensional graphene/mesoporous Fe3O4 nanohybrid for highly sensitive and selective detection of p-nitrophenol. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 266, 86–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SNB.2018.03.059
Rinaudo, M. (2006). Chitin and chitosan: Properties and applications. Progress on Polymer Science, 31, 603–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2006.06.001
Santos, V. P., Marques, N. S. S., Maia, P. C. S. V., de Lima, M. A. B., Franco, L. de O., & de Campos-Takaki, G. M. (2020). Seafood Waste as Attractive Source of Chitin and Chitosan Production and Their Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(12), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJMS21124290
Simsir, H., Eltugral, N., & Karagoz, S. (2017). Hydrothermal carbonization for the preparation of hydrochars from glucose, cellulose, chitin, chitosan and wood chips via low-temperature and their characterization. Bioresource Technology, 246, 82–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.07.018
Singh, A., Benjakul, S., & Prodpran, T. (2019). Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Chitosan from Squid Pen: Molecular Characterization and Fat Binding Capacity. Journal of Food Science, 84(2), 224–234. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.14439
Singh, S., Negi, T., Sagar, N. A., Kumar, Y., Tarafdar, A., Sirohi, R., Sindhu, R., & Pandey, A. (2022). Sustainable processes for treatment and management of seafood solid waste. Science of The Total Environment, 817, 152951. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2022.152951
Soares, S. F., Fernandes, T., Trindade, T., & Daniel-da-Silva, A. L. (2019). Recent advances on magnetic biosorbents and their applications for water treatment. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 18(1), 151–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10311-019-00931-8
Tao, K., Dou, H., & Sun, K. (2008). Interfacial coprecipitation to prepare magnetite nanoparticles : Concentration and temperature dependence. 320, 115–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2008.01.051
Teixeira-Costa, B. E., & Andrade, C. T. (2021). Chitosan as a Valuable Biomolecule from Seafood Industry Waste in the Design of Green Food Packaging. Biomolecules, 11(11), 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/BIOM11111599
Vakili, M., Rafatullah, M., Ibrahim, M. H., & Abdullah, A. Z. (2016). Preparation of Chitosan Beads for the Adsorption of Reactive Blue 4 from Aqueous Solutions. Iranica Journal of Energy and Environment, January. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.ijee.2016.07.02.06
Yarnpakdee, S., Kaewprachu, P., Jaisan, C., Senphan, T., Nagarajan, M., & Wangtueai, S. (2022). Extraction and Physico–Chemical Characterization of Chitosan from Mantis Shrimp (Oratosquilla nepa) Shell and the Development of Bio-Composite Film with Agarose. Polymers, 14(19), 3983. https://doi.org/10.3390/POLYM14193983
Yazdani, F., & Edrissi, M. (2010). Effect of pressure on the size of magnetite nanoparticles in the coprecipitation synthesis. Materials Science & Engineering B, 171(1–3), 86–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2010.03.077
Young, D. M., & Cabezas, H. (1999). Designing sustainable processes with simulation: the waste reduction (WAR) algorithm. Computers and Chemical Engineering, 23, 1477–1491.
Zhou, L., Liu, J., & Liu, Z. (2009). Adsorption of platinum ( IV ) and palladium ( II ) from aqueous solution by thiourea-modified chitosan microspheres. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 172, 439–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.07.030
Zuorro, A., Moreno-Sader, K. A., & González-Delgad, Á. D. (2021). Inherent Safety Analysis and Sustainability Evaluation of Chitosan Production from Shrimp Exoskeleton in Colombia. Water, 13(4), 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/W13040553

 PDF
PDF
 FLIP
FLIP