Geopolymers from construction and demolition glass waste: a review of technological trends and sustainable applications
Geopolímeros a partir de residuos de vidrio de construcción y demolición: una revisión de tendencias tecnológicas y aplicaciones sostenibles
Barra lateral del artículo
Términos de la licencia (VER)

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
Declaración del copyright
Los autores ceden en exclusiva a la Universidad EIA, con facultad de cesión a terceros, todos los derechos de explotación que deriven de los trabajos que sean aceptados para su publicación en la Revista EIA, así como en cualquier producto derivados de la misma y, en particular, los de reproducción, distribución, comunicación pública (incluida la puesta a disposición interactiva) y transformación (incluidas la adaptación, la modificación y, en su caso, la traducción), para todas las modalidades de explotación (a título enunciativo y no limitativo: en formato papel, electrónico, on-line, soporte informático o audiovisual, así como en cualquier otro formato, incluso con finalidad promocional o publicitaria y/o para la realización de productos derivados), para un ámbito territorial mundial y para toda la duración legal de los derechos prevista en el vigente texto difundido de la Ley de Propiedad Intelectual. Esta cesión la realizarán los autores sin derecho a ningún tipo de remuneración o indemnización.
La autorización conferida a la Revista EIA estará vigente a partir de la fecha en que se incluye en el volumen y número respectivo en el Sistema Open Journal Systems de la Revista EIA, así como en las diferentes bases e índices de datos en que se encuentra indexada la publicación.
Todos los contenidos de la Revista EIA, están publicados bajo la Licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-NoDerivativa 4.0 Internacional
Licencia
![]()
Esta obra está bajo una Licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-NoDerivativa 4.0 Internacional
Contenido principal del artículo
Resumen
Recycled glass from construction and demolition waste has emerged as a promising precursor in geopolymer production, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional Portland cement. This review synthesizes recent technological advancements and environmental benefits associated with glass-based geopolymers. Key findings reveal that incorporating recycled glass enhances compressive strength, durability, and thermal resistance, while significantly reducing carbon emissions compared to conventional cementitious materials. However, challenges remain due to the variability in glass chemical composition, which can negatively impact geopolymerization processes, leading to inconsistencies in the final product's performance. The review further explores how the integration of additives such as fibers, silica fume, and nanoparticles can mitigate these challenges by improving mechanical properties, including tensile and flexural strength, and enhancing chemical stability. These enhancements are critical in extending the potential applications of geopolymers in aggressive environments. Additionally, the use of recycled glass in geopolymer matrices contributes to significant waste valorization, effectively lowering the demand for virgin raw materials and reducing the environmental burden associated with landfill accumulation. The reduction in energy consumption, particularly by avoiding the high-temperature processes typical of Portland cement production, further amplifies the sustainability of glass-based geopolymers. Despite these environmental and mechanical advantages, technical barriers, including the need for more effective glass sorting and pre-treatment methods, continue to limit widespread adoption. Future research should focus on optimizing geopolymer formulations, improving processing techniques, and scaling up production processes to meet the demands of industrial-scale applications. This review concludes that recycled glass-based geopolymers offer a viable and eco-friendly solution for the construction industry, providing a key pathway toward more sustainable building practices and reducing the overall environmental footprint of construction materials.
Descargas
Detalles del artículo
Sandra Milena Velásquez Restrepo, Servicio Nacional de Aprendizaje (SENA), Colombia
Magister en Ingeniería, Bioingeniera, Ingeniera Industrial
Referencias (VER)
Ahmed, H. U., Mahmood, L. J.., Muhammad, M. A., Faraj, R., Qaidi, S. M.A., Hamah Sor, N., Mohammed, A. S., Mohammed, A. A. (2022). Geopolymer concrete as a cleaner construction material: An overview on materials and structural performances. Cleaner Materials. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. clema.2022.100111
Ahmed, H. U., Mohammed, A. S., Faraj, R. H., Qaidi, S. M., and Mohammed, A. A. (2022). Compressive strength of geopolymer concrete modified with nano-silica: Experimental and modeling investigations. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 16, e01036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscm.2022.e01036
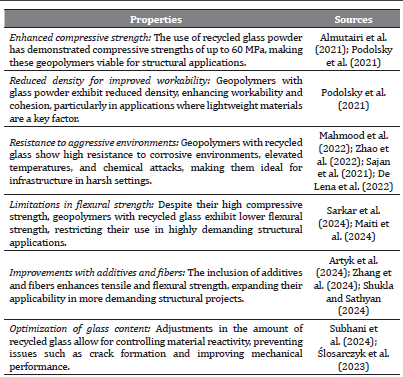
Almutairi, A. L., Tayeh, B. A., Adesina, A., Isleem, H. F., and Zeyad, A. M. (2021). Potential applications of geopolymer concrete in construction: A review. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 15, e00733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. cscm.2021.e00733
Alrefaei, Y., Wang, Y.-S., Dai, J.-G., and Xu, Q.-F. (2020). Effect of superplasticizers on properties of one-part Ca(OH)2/Na2SO4 activated geopolymer pastes. Construction and Building Materials, 241, 117990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. conbuildmat.2019.117990
Amer, O. A., Rangaraju, P., Konduru, H., and Hussein, H. Z. (2023). Sustainable cement alternatives utilizing geopolymer for use in full depth reclamation of asphalt pavements. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 24(2), 2103132. https://doi.org/10.1080/10298436.2022.2103132
Amiri, A., Toufigh, M. M., and Toufigh, V. (2023). Recycling and utilization assessment of municipal solid waste materials to stabilize aeolian sand. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 27(3), 1042-1053. https://doi.org/10.1007/ s12205-022-1418-1
Amran, Y. M., Alyousef, R., Alabduljabbar, H., and El-Zeadani, M. (2020). Clean production and properties of geopolymer concrete: A review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 251, 119679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119679
Ardhira, P. J., Shukla, S. K., and Sathyan, D. (2024). Thermo-mechanical behaviour of newly developed fabric-reinforced engineered geopolymer mortar. Construction and Building Materials, 440, 137441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. conbuildmat.2024.137441
Artyk, Z., Kuan, Y., Zhang, D., Shon, C. S., Ogwumeh, C. M., and Kim, J. (2024). Development of engineered geopolymer composites containing low-activity fly ashes and ground granulated blast furnace slags with hybrid fibers. Construction and Building Materials, 422, 135760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. conbuildmat.2024.135760
Atoyebi Olumoyewa, D., Iwuozor Kingsley, O., Emenike Ebuka, C., Anamayi David, S., and Adeniyi Adewale, G. (2023). Physical and mechanical properties of locally fabricated geopolymer-plastic ceiling boards. Results in Engineering, 101, 101230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rineng.2023.101230
Bernardo, E., Elsayed, H., Mazzi, A., Tameni, G., Gazzo, S., and Contrafatto, L. (2022). Double-life sustainable construction materials from alkali activation of volcanic ash/discarded glass mixture. Construction and Building Materials, 359, 129540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.129540
Bompa, D. V., Xu, B., and Corbu, O. (2022). Evaluation of one-part slag–fly-ash alkali-activated mortars incorporating waste glass powder. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 34(12), 05022001. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE) MT.1943-5533.0004532
Cakmak, T., Ustabas, I., Kurt, Z., and Gurbuz, A. (2024). The importance of early strength in structural applications: Obsidian-based geopolymer mortars and silica fume substitution study. Structural Concrete. https://doi.org/10.1002/ suco.202400726
Dadsetan, S., Siad, H., Lachemi, M., Mahmoodi, O., and Sahmaran, M. (2022). Sodium glass liquid from glass waste as a user-friendly hardener in structural geopolymer systems. Cement and Concrete Composites, 130, 104525. https:// doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2022.104525
Danish, A., and Torres, A. S. (2024). Geopolymerization of non-metallic fractions of electronic waste: A sustainable disposal strategy? Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, 100930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsc.2024.100930
De Azevedo, A. R., Marvila, M. T., Ali, M., Khan, M. I., Masood, F., and Vieira, C. M. F. (2021). Effect of the addition and processing of glass polishing waste on the durability of geopolymeric mortars. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 15, e00662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscm.2021.e00662
De Lena, E., et al. (2022). Integrated calcium looping system with circulating fluidized bed reactors for low CO2 emission cement plants. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. ijggc.2021.103555
Demiral, N. C., Ekinci, M. O., Sahin, O., Ilcan, H., Kul, A., Yildirim, G., and Sahmaran, M. (2022). Mechanical anisotropy evaluation and bonding properties of 3D-printable construction and demolition waste-based geopolymer mortars. Cement and Concrete Composites, 134, 104814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. cemconcomp.2022.104814
Epure, C., Munteanu, C., Istrate, B., Harja, M., and Buium, F. (2023). Applications of recycled and crushed glass (RCG) as a substitute for natural materials in various fields—A review. Materials, 16(17), 5957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ ma16175957
Eskisar, T. (2022, September). Strength Properties of Coffee Waste with Recycled Glass Geopolymers. In International Conference on Environmental Geotechnology, Recycled Waste Materials and Sustainable Engineering (pp. 117-124). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore.
Girish, M. G., Shetty, K. K., and Nayak, G. (2023). Effect of slag sand on mechanical strengths and fatigue performance of paving grade geopolymer concrete. International Journal of Pavement Research and Technology, 1-18. https://doi. org/10.1007/s42947-023-00363-2
Hamzah, H. K., Huseien, G. F., Asaad, M. A., Georgescu, D. P., Ghoshal, S. K., and Alrshoudi, F. (2021). Effect of waste glass bottles-derived nanopowder as slag replacement on mortars with alkali activation: Durability characteristics. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 15, e00775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. cscm.2021.e00775
Hassan, A., ElNemr, L., Goebel, C., and Koenke, C. (2024). Effect of hybrid polypropylene fibers on mechanical and shrinkage behavior of alkali-activated slag concrete. Construction and Building Materials, 411, 134485. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.134485
He, P., Zhang, B., Lu, J. X., and Poon, C. S. (2021). Reaction mechanisms of alkali-activated glass powder-ggbs-CAC composites. Cement and Concrete Composites, 122, 104143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. cemconcomp.2021.104143
Ilcan, H., Sahin, O., Kul, A., Ozcelikci, E., and Sahmaran, M. (2023). Rheological property and extrudability performance assessment of construction and demolition waste-based geopolymer mortars with varied testing protocols. Cement and Concrete Composites, 136, 104891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. cemconcomp.2022.104891
Khalaf, K. Y., and Mahmood, K. R. (2024). Sustainable use of recycled glass powder-based geopolymer of organic soil stabilization. Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología- Serie de Conferencias, 3, 857-857. https://doi.org/10.56294/sctconf2024857
Khan, S. A., Kul, A., Şahin, O., Şahmaran, M., Al-Ghamdi, S. G., and Koç, M. (2022). Energy-environmental performance assessment and cleaner energy solutions for a novel Construction and Demolition Waste-based geopolymer binder production process. Energy Reports, 8, 14464-14475. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.egyr.2022.10.345
Kumar, A. S., Muthukannan, M., Irene, A., Arun, K. K., and Ganesh, A. C. (2022). Flexural behaviour of reinforced geopolymer concrete incorporated with hazardous heavy metal waste ash and glass powder. Materials Science Forum, 1048, 345. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.1048.345
Lee, S., Chun, B., Kim, G., Lee, S. W., and Yoo, D. (2023). Tensile Performance of Slag- LCDGP Based Geopolymer Reinforced With PE Fiber. In 8th World Congress on Civil, Structural, and Environmental Engineering, CSEE 2023. Avestia Publishing. https://doi.org/10.11159/icsect23.107
Mancin, S., Sguanci, M., Anastasi, G., Godino, L., Lo Cascio, A., Morenghi, E., Piredda, M., and De Marinis, M. G. (2024). A methodological framework for rigorous systematic reviews: Tailoring comprehensive analyses to clinicians and healthcare professionals. Methods, 225, 38-43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. ymeth.2024.03.006
Manzoor, T., Bhat, J. A., and Shah, A. H. (2024). Performance of geopolymer concrete at elevated temperature− A critical review. Construction and Building Materials, 420, 135578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.135578
Mendes, B. C., Pedroti, L. G., Vieira, C. M. F., Carvalho, J. M. F., Ribeiro, J. C. L., Albuini-Oliveira, N. M., and Andrade, I. K. R. (2022). Evaluation of eco-efficient geopolymer using chamotte and waste glass-based alkaline solutions. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 16, e00847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. cscm.2021.e00847
Mir, N., Khan, S. A., Kul, A., Şahin, O., Ozcelikci, E., Şahmaran, M., and Koç, M. (2023). Construction and demolition waste-based self-healing geopolymer composites for the built environment: An environmental profile assessment and optimization. Construction and Building Materials, 369, 130520. https:// doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.130520
Neupane, K. (2022). Evaluation of environmental sustainability of one-part geopolymer binder concrete. Cleaner Materials, 6, 100138. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.clema.2022.100138
Neves, J., and Freire, A. C. (2022). Special Issue “The use of recycled materials to promote pavement sustainability performance”. Recycling, 7(2), 12. https:// doi.org/10.3390/recycling7020012
Ozcelikci, E., Ozdogru, E., Tugluca, M. S., Ilcan, H., and Şahmaran, M. (2024). Comprehensive investigation of performance of construction and demolition waste based wood fiber reinforced geopolymer composites. Journal of Building Engineering, 84, 108682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2024.108682
Podolsky, Z., Liu, J., Dinh, H., Doh, J. H., Guerrieri, M., and Fragomeni, S. (2021). State of the art on the application of waste materials in geopolymer concrete. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 15, e00637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. cscm.2021.e00637
Raad Shaker, H., AlSaraj, W., and Al-Jaberi, L. A. (2024). Behavior of reinforced geopolymer concrete beams under repeated load. International Journal of Engineering, 37(5), 974-983. https://doi.org/10.5829/ije.2024.37.05b.14
Rajaee, K., Bilondi, M. P., Barimani, M. H., Daluee, M. A., and Zaresefat, M. (2024). Effect of gradations of glass powder on engineering properties of clay soil geopolymer. Case Studies in Construction Materials, e03403. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.cscm.2024.e03403
Ramadan, M., Kohail, M., Alharbi, Y. R., Abadel, A. A., Binyahya, A. S., and Mohsen, A. (2023). Investigation of autoclave curing impact on the mechanical properties, heavy metal stabilization and anti-microbial activity of the green geopolymeric composite based on received/thermally-treated glass polishing sludge. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 23, 2672-2689. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.01.158
Ramezani, S. J., Toufigh, M. M., and Toufigh, V. (2023). Utilization of glass powder and silica fume in sugarcane bagasse ash-based geopolymer for soil stabilization. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 35(4), 04023042. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0004704
Raut, A., Singh, R. J., and Kannan, Y. S. (2023). Insulation behavior of foamed based geopolymer as a thermally efficient sustainable blocks. Materials Today: Proceedings. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2023.03.022
Ríos, L. M. H., Triviño, A. F. H., Villaquirán-Caicedo, M. A., and de Gutiérrez, R. M. (2023). Effect of the use of waste glass (as precursor, and alkali activator) in the manufacture of geopolymer rendering mortars and architectural tiles. Construction and Building Materials, 363, 129760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. conbuildmat.2022.129760
Sajan, P., et al. (2021). Combined effect of curing temperature, curing period and alkaline concentration on the mechanical properties of fly ash-based geopolymer. Cleaner Materials. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clema.2021.100002
Santana-Carrillo, J. L., Burciaga-Díaz, O., and Escalante-Garcia, J. I. (2022). Blended limestone-Portland cement binders enhanced by waste glass based and commercial sodium silicate-effect on properties and CO2 emissions. Cement and Concrete Composites, 126, 104364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. cemconcomp.2021.104364
Sarkar, M., Maiti, M., Malik, M. A., and Xu, S. (2024). Waste valorization: Sustainable geopolymer production using recycled glass and coal industry by-product fly ash at ambient temperature. Chemical Engineering Journal, 153144. https:// doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.153144
Schmitz, A., Kamiński, J., Maria Scalet, B., and Soria, A. (2011). Consumo energético y emisiones de CO2 de la industria europea del vidrio. Energy Policy, 39(1), 142-155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2010.09.022
Shiwa, S., Khosravi, A., Mohammadi, F., Abbasi, M., and Sillanpää, M. (2024). The capacity of alkali‐activated industrial wastes in novel sustainable ceramic membranes. ChemBioEng Reviews. https://doi.org/10.5829/ IJE.2024.37.05B.14
Singh, N. B., and et al. (2020). Geopolymers as an alternative to Portland cement: An overview. Construction and Building Materials, 250, 118889. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118889
Ślosarczyk, A., Fořt, J., Klapiszewska, I., Thomas, M., Klapiszewski, Ł., and Černý, R. (2023). A literature review of the latest trends and perspectives regarding alkali-activated materials in terms of sustainable development. Journal of Materials Research and Technology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. jmrt.2023.07.038
Stepien, A., and Wojarska-Gniady, P. (2023). Recycling in construction-characteristics of composite and recycled materials used in structural elements of buildings. International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference: SGEM, 23(4.2), 61-69. https://doi.org/10.5593/sgem2023V/4.2/s18.08
Subhani, M., Ali, S., Allan, R., Grace, A., and Rahman, M. (2024). Physical and mechanical properties of self-compacting geopolymer concrete with waste glass as partial replacement of fine aggregate. Construction and Building Materials, 437, 136956.
Taher, S. M., Saadullah, S. T., Haido, J. H., and Tayeh, B. A. (2021). Behavior of geopolymer concrete deep beams containing waste aggregate of glass and limestone as a partial replacement of natural sand. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 15, e00744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscm.2021. e00744
Tajaddini, A., Saberian, M., Sirchi, V. K., Li, J., and Maqsood, T. (2023). Improvement of mechanical strength of low-plasticity clay soil using geopolymer-based materials synthesized from glass powder and copper slag. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 18, e01820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscm.2022. e01820
Wu, J. L., Zhang, X., Xie, J., Kou, S., Luo, Q., Wei, J., Lin, C., and Feng, G.-L. (2022). Recycling of waste cathode ray tube glass through fly ash-slag geopolymer mortar. Construction and Building Materials, 322, 126454. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.126454
Xu, Z., Li, J., Qian, H., and Wu, C. (2022). Blast resistance of hybrid steel and polypropylene fibre reinforced ultra-high performance concrete after exposure to elevated temperatures. Composite Structures, 294, 115771. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.115771
Yildirim, G., Ashour, A., Ozcelikci, E., Gunal, M. F., Ozel, B. F., and Alhawat, M. M. (2023). Development of ambient-cured geopolymer mortars with construction and demolition waste-based materials. Northwest Journal, S2-008. https://doi. org/10.17756/nwj.2023-s2-008
Yilmaz, Y., Cakmak, T., Kurt, Z., and Ustabas, I. (2024). Predicting mechanical properties in geopolymer mortars, including novel precursor combinations, through XGBoost method. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 1-25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-024-09179-z
Zareechian, M., Siad, H., Lachemi, M., and Sahmaran, M. (2023). Advancements in cleaner production of one-part geopolymers: A comprehensive review of mechanical properties, durability, and microstructure. Construction and Building Materials, 409, 133876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. conbuildmat.2023.133876
Zhang, H., He, B., Chen, W., Ai, J., Zhu, X., and Jiang, Z. (2024). Investigating the influence of fibre type and content on the toughness and ductility of geopolymer mortar with acoustic emission technology. Cement and Concrete Composites, 147, 105434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. cemconcomp.2024.105434
Zhao, J., and Li, S. (2022). Study on processability, compressive strength, drying shrinkage and evolution mechanisms of microstructures of alkali-activated slag-glass powder cementitious material. Construction and Building Materials, 344, 128196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.128196
Zuaiter, M., El-Hassan, H., El-Maaddawy, T., El-Ariss. B. (2022) Properties of slag-fly ash blended geopolymer concrete reinforced with hybrid glass fibers. Buildings, 12 (8), p. 1114 https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12081114

 PDF
PDF
 FLIP
FLIP