Detección de dolor apartir de señales de EEG
Pain detection evaluated from electroencephalographic signals
Barra lateral del artículo
Términos de la licencia (VER)

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
Declaración del copyright
Los autores ceden en exclusiva a la Universidad EIA, con facultad de cesión a terceros, todos los derechos de explotación que deriven de los trabajos que sean aceptados para su publicación en la Revista EIA, así como en cualquier producto derivados de la misma y, en particular, los de reproducción, distribución, comunicación pública (incluida la puesta a disposición interactiva) y transformación (incluidas la adaptación, la modificación y, en su caso, la traducción), para todas las modalidades de explotación (a título enunciativo y no limitativo: en formato papel, electrónico, on-line, soporte informático o audiovisual, así como en cualquier otro formato, incluso con finalidad promocional o publicitaria y/o para la realización de productos derivados), para un ámbito territorial mundial y para toda la duración legal de los derechos prevista en el vigente texto difundido de la Ley de Propiedad Intelectual. Esta cesión la realizarán los autores sin derecho a ningún tipo de remuneración o indemnización.
La autorización conferida a la Revista EIA estará vigente a partir de la fecha en que se incluye en el volumen y número respectivo en el Sistema Open Journal Systems de la Revista EIA, así como en las diferentes bases e índices de datos en que se encuentra indexada la publicación.
Todos los contenidos de la Revista EIA, están publicados bajo la Licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-NoDerivativa 4.0 Internacional
Licencia
![]()
Esta obra está bajo una Licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-NoDerivativa 4.0 Internacional
Contenido principal del artículo
Resumen
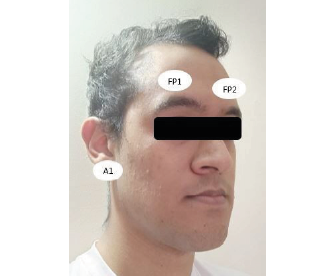
La evaluación de dolor es de gran importancia en el campo de la medicina ya que permite detectar condiciones médicas o definir la manera en la que se debe tratar. Su evaluación se basa en primera instancia en información que el mismo paciente entrega. Sin embargo, en algunos casos en los que el paciente no tiene la capacidad de expresarlo, resulta de gran utilidad métodos que permitan evaluarlo. En este artículo se propone la evaluación de presencia o ausencia de dolor a partir de características asociadas a señales electro-encefalográficas en un experimento en el que se induce dolor agudo a 14 participantes con una prueba de electro-diagnóstico, en hombres y mujeres con edades entre 18 y 33 años. Se utilizan redes neuronales para la clasificación, obteniendo una exactitud del 74,19 %.
Descargas
Detalles del artículo
Referencias (VER)
Grabowski, S. R., & Tortora, G. J. (2000). Principles of anatomy and physiology. New York/Chichester: Wiley.
Tortora, G. J., & Nielsen, M. T. (1995). Human Anatomy. Harper Collins College Pub.
Ilana, E. (1979). Pain terms; a list with definitions and notes on usage. Pain, 6, 249.
Manworren, R. C., & Stinson, J. (2016). Pediatric pain measurement, assessment, and evaluation. In Seminars in pediatric neurology (Vol. 23, No. 3, pp. 189-200). WB Saunders. DOI: https: / / doi .org /10.1016/j.spen.2016.10.001.
Kagita, J., & Mitsukura, Y. (2018). Quantification of pain degree by frequency features of single-chanelled EEG. In 2018 IEEE 15th International Workshop on Advanced Motion Control (AMC) (pp. 359-363). IEEE.
Tatum IV, W. O. (2021). Handbook of EEG interpretation. Springer Publishing Company.
Bonotis, P. A., Tsouros, D. C., Smyrlis, P. N., Tzallas, A. T., Giannakeas, N., Glavas, E., & Tsipouras, M. G. (2019). Automated Assessment of Pain Intensity based on EEG Signal Analysis. In 2019 IEEE 19th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering (BIBE) (pp. 583-588). IEEE.
Panavaranan, P., & Wongsawat, Y. (2013). EEG-based pain estimation via fuzzy logic and polynomial kernel support vector machine. In The 6th 2013 Biomedical Engineering International Conference (pp. 1-4). IEEE.
Nir, R. R., Sinai, A., Raz, E., Sprecher, E., & Yarnitsky, D. (2010). Pain assessment by continuous EEG: association between subjective perception of tonic pain and peak frequency of alpha oscillations during stimulation and at rest. Brain research, 1344, 77-86.
Cao, T., Wang, Q., Liu, D., Sun, J., & Bai, O. (2020). Resting state EEG-based sudden pain recognition method and experimental study. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 59, 101925.
Tatum IV, W. O. (2021). Handbook of EEG interpretation. Springer Publishing Company.
Bai, Y., Hu, Y., & Zhang, Z. (2016). Spontaneous EEG-based normalization of pain-evoked neural responses: Effect on improving the accuracy of pain prediction. In 2016 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Virtual Environments for Measurement Systems and Applications (CIVEMSA) (pp. 1-4). IEEE.
Yu, M., Sun, Y., Zhu, B., Zhu, L., Lin, Y., Tang, X., ... & Dong, M. (2020). Diverse frequency band-based convolutional neural networks for tonic cold pain assessment using EEG. Neurocomputing, 378, 270-282.
Artículos similares
- Javier Eduardo Diaz Zamboni, Justo García, Lautaro Caupolicán Ré, Santiago Salinas Sosa, Diana Carolina Vertiz del Valle, Juan Francisco Rizzato, Juan Manuel Cabrera, César Iván González, Jordán Francisco Insfrán, Mejora de Prácticas en Desarrollo de Software en un Contexto Universitario de I+D+I , Revista EIA: Vol. 22 Núm. 44 (2025): Tabla de contenido Revista EIA No. 44
- Guillermo-de-Jesús Hoyos-Rivera, José-Clemente Hernández-Hernández, Pensamiento computacional y ChatGPT , Revista EIA: Vol. 21 Núm. 42 (2024): Tabla de contenido Revista EIA No. 42
También puede {advancedSearchLink} para este artículo.

 PDF
PDF
 FLIP
FLIP